0. 背景
最近折腾腾讯云轻量香港服务器,然而公司内网由于一些特殊设置,无法直接SSH到境外服务器上,不得已通过自己一个位于北京的VPS节点进行中转,经过一些查阅整理,总结了几个小技巧。
1. VSCode Remote通过中转节点连接目标服务器
VSCode的远程开发套件在『使用Docker作为C++开发环境:适用于CLion与VSCode的配置』里略有介绍。配置起来很简单,但如果需要使用中转怎么办呢?(以Windows场景为例)
例如我有一个1.1.1.1作为中转节点,有一个2.2.2.2是我的目标节点。那么需要点左下角打开远程开发工具,选择这里编辑.ssh_config:
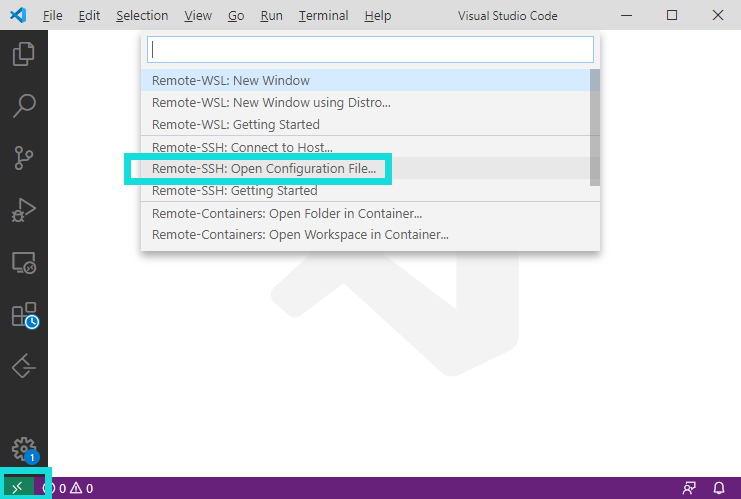
Host jump_box
HostName 1.1.1.1
User user
Host target
HostName 2.2.2.2
User
ProxyCommand C:\Windows\System32\OpenSSH\ssh.exe jump_box netcat -w 120 %h %p这里的原理是使用jump_box的netcat进行转发,只要提前在1.1.1.1和2.2.2.2上的~/.ssh/authorized_keys里添加好本机的SSH Public Key即可。
2. Windows Terminal中配置SSH Keep-alive
Windows Terminal由微软开发,是Windows下非常好用、几乎超过所有其他命令行的一个终端工具。
在Windows Terminal中,可以添加一个默认操作的链接选项,添加如下配置,效果如上图所示。
"list":
[{
"guid": "{b453ae62-4e3d-5e58-b989-0a998ec44144}",
"name": "graueneko.com",
"tabTitle": "graueneko.com",
"commandline": "ssh -o ServerAliveInterval=60 ubuntu@graueneko.com",
"cursorShape": "filledBox",
"icon": "ms-appx:///ProfileIcons/{574e775e-4f2a-5b96-ac1e-a2962a402336}.png"
},
...
]由于网络中间常常有些中转服务器在链接太久没有数据传输时强制中断掉,因此为避免这种情况,这里使用了`ssh -o ServerAliveInterval=60"来为SSH每60秒发送一次心跳包,保持SSH有数据传输避免被中断。
3. Windows Terminal配色
在Windows Terminal的settings.json中,可以添加如下配色选项(使用的是OneDark Theme),让命令行更好看些:
{
"schemes": [
{
"name": "OneHalfDark",
"black": "#282c34",
"red": "#e06c75",
"green": "#98c379",
"yellow": "#e5c07b",
"blue": "#61afef",
"purple": "#c678dd",
"cyan": "#56b6c2",
"white": "#dcdfe4",
"brightBlack": "#282c34",
"brightRed": "#e06c75",
"brightGreen": "#98c379",
"brightYellow": "#e5c07b",
"brightBlue": "#61afef",
"brightPurple": "#c678dd",
"brightCyan": "#56b6c2",
"brightWhite": "#dcdfe4",
"background": "#282c34",
"foreground": "#dcdfe4"
}
],
}添加的位置如下: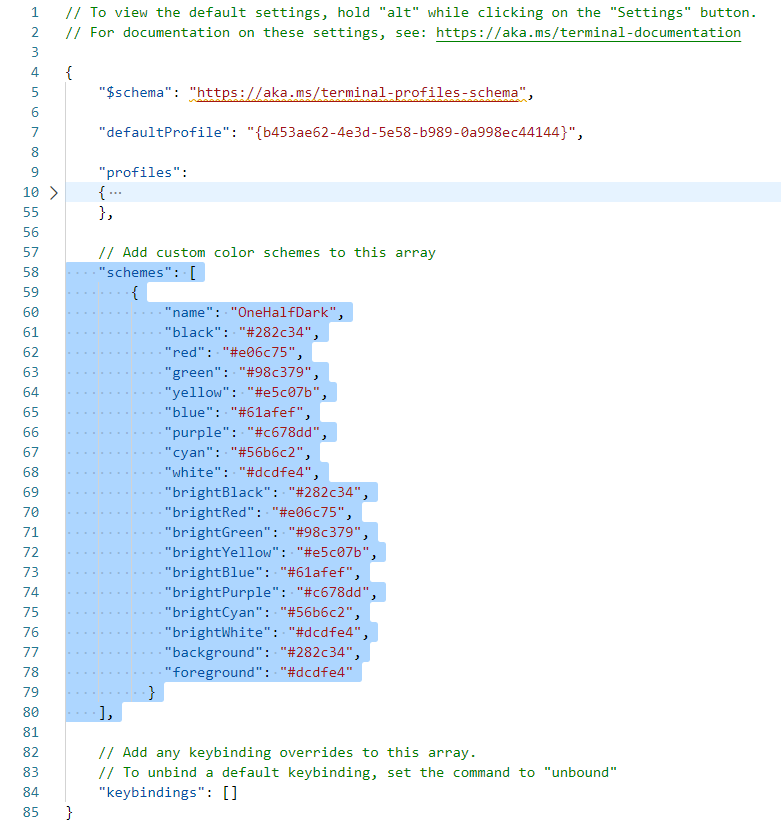
4. SSH连接接后加载颜色文件
我很喜欢腾讯云自带的~/.bashrc文件配色,效果如下,可执行文件为绿色,文件夹为蓝色,普通文件是白色,正常软链接为青色,出错的软链接为红色,等等: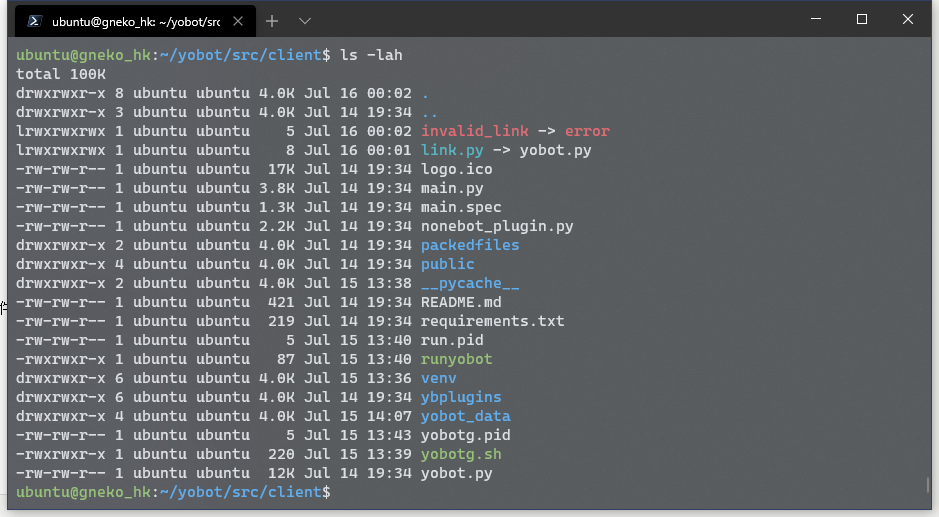
没有这个~/.bashrc配置的同学可以使用这里的文件(我直接把它抄过来了)
# ~/.bashrc: executed by bash(1) for non-login shells.
# see /usr/share/doc/bash/examples/startup-files (in the package bash-doc)
# for examples
# If not running interactively, don't do anything
case $- in
*i*) ;;
*) return;;
esac
# don't put duplicate lines or lines starting with space in the history.
# See bash(1) for more options
#HISTCONTROL=ignoreboth
# append to the history file, don't overwrite it
shopt -s histappend
# for setting history length see HISTSIZE and HISTFILESIZE in bash(1)
#HISTSIZE=1000
HISTFILESIZE=2000
# check the window size after each command and, if necessary,
# update the values of LINES and COLUMNS.
shopt -s checkwinsize
# If set, the pattern "**" used in a pathname expansion context will
# match all files and zero or more directories and subdirectories.
#shopt -s globstar
# make less more friendly for non-text input files, see lesspipe(1)
[ -x /usr/bin/lesspipe ] && eval "$(SHELL=/bin/sh lesspipe)"
# set variable identifying the chroot you work in (used in the prompt below)
if [ -z "${debian_chroot:-}" ] && [ -r /etc/debian_chroot ]; then
debian_chroot=$(cat /etc/debian_chroot)
fi
# set a fancy prompt (non-color, unless we know we "want" color)
case "$TERM" in
xterm-color|*-256color) color_prompt=yes;;
esac
# uncomment for a colored prompt, if the terminal has the capability; turned
# off by default to not distract the user: the focus in a terminal window
# should be on the output of commands, not on the prompt
#force_color_prompt=yes
if [ -n "$force_color_prompt" ]; then
if [ -x /usr/bin/tput ] && tput setaf 1 >&/dev/null; then
# We have color support; assume it's compliant with Ecma-48
# (ISO/IEC-6429). (Lack of such support is extremely rare, and such
# a case would tend to support setf rather than setaf.)
color_prompt=yes
else
color_prompt=
fi
fi
if [ "$color_prompt" = yes ]; then
PS1='${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\[\033[01;32m\]\u@\h\[\033[00m\]:\[\033[01;34m\]\w\[\033[00m\]\$ '
else
PS1='${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\u@\h:\w\$ '
fi
unset color_prompt force_color_prompt
# If this is an xterm set the title to user@host:dir
case "$TERM" in
xterm*|rxvt*)
PS1="\[\e]0;${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\u@\h: \w\a\]$PS1"
;;
*)
;;
esac
# enable color support of ls and also add handy aliases
if [ -x /usr/bin/dircolors ]; then
test -r ~/.dircolors && eval "$(dircolors -b ~/.dircolors)" || eval "$(dircolors -b)"
alias ls='ls --color=auto'
#alias dir='dir --color=auto'
#alias vdir='vdir --color=auto'
alias grep='grep --color=auto'
alias fgrep='fgrep --color=auto'
alias egrep='egrep --color=auto'
fi
# colored GCC warnings and errors
#export GCC_COLORS='error=01;31:warning=01;35:note=01;36:caret=01;32:locus=01:quote=01'
# some more ls aliases
alias ll='ls -alF'
alias la='ls -A'
alias l='ls -CF'
# Add an "alert" alias for long running commands. Use like so:
# sleep 10; alert
alias alert='notify-send --urgency=low -i "$([ $? = 0 ] && echo terminal || echo error)" "$(history|tail -n1|sed -e '\''s/^\s*[0-9]\+\s*//;s/[;&|]\s*alert$//'\'')"'
# Alias definitions.
# You may want to put all your additions into a separate file like
# ~/.bash_aliases, instead of adding them here directly.
# See /usr/share/doc/bash-doc/examples in the bash-doc package.
if [ -f ~/.bash_aliases ]; then
. ~/.bash_aliases
fi
# enable programmable completion features (you don't need to enable
# this, if it's already enabled in /etc/bash.bashrc and /etc/profile
# sources /etc/bash.bashrc).
if ! shopt -oq posix; then
if [ -f /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion ]; then
. /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion
elif [ -f /etc/bash_completion ]; then
. /etc/bash_completion
fi
fi但是仅仅这样还是不能显示颜色,问题在于,SSH连接时并不会加载~/.bashrc文件,只会加载~/.bash_profile,因此要在~/.bash_profile中添加如下内容:
if [ -f ~/.bashrc ]; then
. ~/.bashrc
fi5. 添加HOSTS方便跳转机器
我现在使用一台国内节点作为所有国外节点的中转服务器,但是每一台都有不同的IP,不能一一记住,而且它们即使绑定了域名也很长。为了简化操作,可以在HOSTS里添加别名进行中转。
例如在/etc/hosts中:
127.0.0.1 localhost
1.1.1.1 jump
2.2.2.2 targ这样配置以后,可以直接使用ssh user@targ的方式连接2.2.2.2服务器。